Structure of atom
The concept of atoms, molecules and ions:
Atom is the smallest particle of an element which can take part in a chemical reaction. The word atom is derived from the Greek word Atomos, meaning indivisible; which could not be further destroyed or reduced. Atoms of different elements have various shapes.
Molecule is the smallest particle of a substance that is capable of independent existence, and still retains the chemical properties of that substance. A molecule is formed when two or more atoms are chemically joined together e.g. H2, O2, N2 etc. Thus the number of atoms in a molecule of an element is called its atomicity.
Elements, formula of molecule, atomicity and name
| Element | Formula of molecule | Atomicity | Name |
| Helium
Neon Argon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Chlorine Ozone Phosphorus Sulphur |
He
Ne Ar H2 O2 N2 Cl2 O3 P4 S8 |
1
1 1 2 2 2 2 3 4 8 |
Monoatomic
Monoatomic Monoatomic Diatomic Diatomic Diatomic Diatomic Triatomic Tetratomic Polyatomic |
Dalton’s atomic theory
The idea that elements are made up of atoms is called the atomic theory. In 1808, John Dalton of England put forward his famous atomic theory which states as follows:
- All chemical changes result from the combination or the separation of atoms.
- Atoms cannot be created or destroyed.
- Atoms of different elements can combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds.
- All elements are made up of small indivisible particles called atoms.
- Atoms of the same elements are exactly alike in every aspect and are different from atoms of all other elements.
The modern atomic theory
- All matter is composed of small particles, some of which are electrically neutral, some are positively charged while some are negatively charged.
- Atoms of the same elements are not alike, but may have different masses.
- An element may have atoms with different masses while an atom of the same element with different masses are called isotopes.
- Atoms of different elements can combine together to form molecules.
- The molecules of a compound have definite compositions and structures.
- The molecules of a compound consist of the atoms of the elements that form the molecules.
- Molecules are the smallest particles of compounds that have the properties of the compound.
- Molecules may be further broken down and when this happens, they no longer have the Characteristics of the compound.
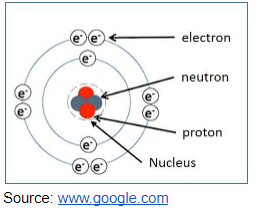
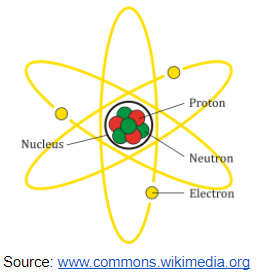
Constituents of the Atom
We have three main particles of an atom which are also regarded as fundamental particles and the particles are proton, electron and neutron.
According to Rutherford’s nuclear theory (1906), the neutron and proton make up the nucleus of the atom. The nucleus is positively charged and surrounded by the electrons in an orbital manner. Atoms are electrically neutral because they contain the same number of electrons and protons.
Properties of fundamental subatomic particles
| Particle | Mass | Charge |
| Proton
Neutron Electron |
1unit
1unit 1/1840 unit |
Positive (+)
Neutral Negative (-) |
Diagram on arrangements of electrons around the nucleus
Atomic number and mass number
The atomic number: it has to do with the number of protons present in the atomic nucleus of the element. It is donated by Z and increased by one when the elements were arranged in order of ascending relative atomic mass.
Note that in neutral atom the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons
Mass number: it is the sum of the protons and the neutrons in the atomic nucleus of the element.
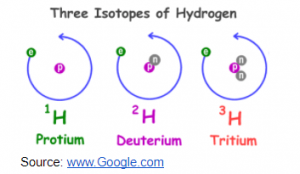
Isotopes: isotopes are atoms with the same atomic number but different mass number.
Relative atomic mass
The relative atomic mass carries no units; it is a ratio given by
= Average mass of 1 atom of element / 1/12th mass of 1 atom of carbon
Note that the relative atomic mass of each element has been verified accurately with the aid of the mass spectrometer introduced by Aston.
Relative molecular
It is the sum of the relative atomic masses of all atoms in one molecule of the substance.
Mole is the amount of substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are carbon atoms in 12grammes of carbon. = Mass in grams / Relative molecular mass
Molar mass of any substance is the mass of one mole of the substance expressed in grams. Its unit is in grams per mole (gmol-1).
Past questions
1.The relative atomic mass of a naturally occurring lithium consisting of 90% Li and 100% Li is ? (Jamb 2018)
A. 6.9
B. 7.1
C. 6.2
D. 6.8
Answer: A
Solution: 90×7/100 + 10×6/100
= 6.3 + 0.6 = 6.9
- How many protons, neutrons and electrons respectively are present in the element 6027Co? (Jamb 2015) A. 27,33 and 33 B. 33,27 and 27 C. 27,33 and 27 D. 60,33 and 60
Answer: C
Solution: remember that atoms that are electrically neutral contains the same number of protons and electrons
Thus 60-27=33. Then neutrons= 33
- How many atoms are there in 0.8g of oxygen molecules? [ O= 16, Na= 6.02×1023mol-1]. (Jamb 2017) A. 1.51×1022 B. 3.01×1021 C. 3.01×1022 D. 1.51×1021
Answer: A
Solution: 6.02×1023×0.8/32
= 1.51×1023atom
- The discovery that protons and neutrons are concentrated at the nucleus of an atom was postulated by ? (Jamb 2015) A. E. Rutherford B. J. Dalton C. J.J. Thomson D. N. Bohr
Answer: A
- How many electrons are in the ion F–? [ 199F]
- 8 (b) 9 (c) 10 (d) 19
Answer: C
Solution: in other to get the number of electrons in the ion subtract the atomic number (9) from the mass number (19) which is equal to 10
- Defined isotopes?
Answer: it can be defined as an atom with the same atomic number but different mass number.
- Defined mass number?
Answer: The mass number of an element is the sum of the protons and the neutrons in the atomic nucleus.
- Name the three fundamental constituents of an atom.
Answer: proton, electron and neutron


No Comments