17.0 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM IN VERTEBRATES
TYPES OF REPRODUCTION
- Sexual Reproduction: Involves the fusion of male and female gametes (sperm and egg).
- Asexual Reproduction: Rare in mammals, but some species can reproduce without fertilization.
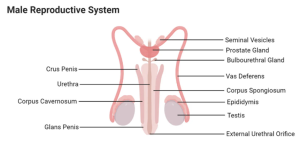
17.1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
- Testes: Produce sperm and hormones like testosterone.
- Epididymis: Stores sperm temporarily until they are matured.
- Vas Deferens: Transports sperm from the epididymis to the urethra.
- Cowper’s gland: Secretes part of the seminal fluid which raises the pH of the female reproductive system.
- Seminal vesicle: Stores sperm until they are ejaculated.
- Seminiferous tubules: They are points where sperms are produced within the testes.
- Prostate gland: Secretes part of the seminal fluid which activates the sperm.
- Urethra: It aids the passage of sperms into the vagina.
- Penis: It helps to introduce sperm into the vagina of the female animal.
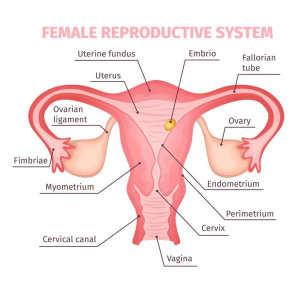
17.2 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
- Ovaries: Produce eggs (ova) and hormones like oestrogen and progesterone.
- Fallopian Tubes/Oviduct: Transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus; site of fertilization.
- Uterus/Womb: Where the fertilized egg implants and develops into a foetus.
- Vagina: Birth canal and the passage for sperm during mating.
- Cervix: It controls the opening and closing of the vagina especially during birth.
- Clitoris: It helps to Stimulate the female during sexual intercourse.
- Vulva: It permits the passage of foetus during birth.
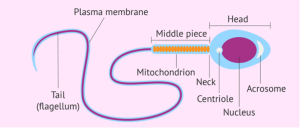
17.3 STRUCTURES OF THE MAMMALIAN GAMETE – MALE GAMETE (SPERM)
- Head: Contains the nucleus, which holds the genetic material (DNA). The head is capped by the acrosome, which contains enzymes that help the sperm penetrate the egg during fertilization.
- Midpiece: Packed with mitochondria that provide the energy needed for the sperm’s motility (movement).
- Tail (Flagellum): A long, whip-like structure that propels the sperm forward, allowing it to swim towards the egg.
STRUCTURES OF THE SPERM CELL SIZE – Sperm are among the smallest cells in the human body, measuring about 50-60 micrometres in length.
SPERM CELL PRODUCTION – Sperm are produced in the testes through a process called spermatogenesis, which occurs in the seminiferous tubules.
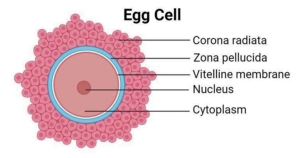
17.4 STRUCTURES OF THE MAMMALIAN GAMETE – FEMALE GAMETE (OVUM)
- Cytoplasm: The ovum has a large amount of cytoplasm, which contains nutrients and organelles necessary for the early stages of development after fertilization
- Nucleus: Contains the genetic material (DNA) of the female.
- Zona Pellucida: A thick, protective glycoprotein layer surrounding the ovum that plays a crucial role in fertilization by allowing only sperm to bind and penetrate.
STRUCTURES OF THE OVUM-SIZE: The ovum is one of the largest cells in the human body, measuring about 100 micrometres in diameter.
OVUM-PRODUCTION – Ova are produced in the ovaries through a process called oogenesis, which results in the formation of a single mature egg from each ovarian cycle.
17.5 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MAMMALIAN MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
- Size: The ovum is significantly larger than the sperm.
- Mobility: Sperm are motile and can swim, while ova are non-motile and are transported through the female reproductive tract.
- Quantity: Males produce millions of sperm daily, while females typically release one ovum per menstrual cycle.
17.6 FERTILIZATION, PREGNANCY AND BIRTH IN HUMANS
FERTILIZATION – Fertilization is the process where a sperm cell from the male fuses with an egg cell (ovum) from the female to form a zygote. It typically occurs in the fallopian tubes of the female reproductive system.
FERTILIZATION PROCESS
- Sperm Capacitation: Sperms undergo changes that enhance their ability to penetrate the egg.
- Acrosome Reaction: The acrosome of the sperm releases enzymes that help it penetrate the zona pellucida of the ovum.
- Fusion: Once a sperm successfully penetrates the egg, the membranes fuse, and the genetic material from both gametes combines to form a zygote.
- Zygote Formation: The zygote contains a complete set of chromosomes (46 in humans) and begins to divide through mitosis.
PREGNANCY – Pregnancy is the period during which a fertilized egg develops into a foetus inside the uterus. Human pregnancy typically lasts about 40 weeks, divided into three trimesters.
PREGNANCY STAGES
- Implantation: The zygote develops into a blastocyst and implants itself into the uterine lining about 6-10 days after fertilization
- Embryonic Development: The first trimester involves the development of major organs and structures. The embryo is most vulnerable during this stage.
- Foetal Development: In the second and third trimesters, the foetus grows and matures, with further development of organs and systems.
PREGNANCY HORMONAL CHANGES: Pregnancy is regulated by hormones such as Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG), progesterone, and oestrogen, which support the pregnancy and prepare the body for childbirth.
BIRTH – Birth is the process of delivering the baby from the uterus to the outside world.
BIRTH STAGES OF LABOR
- First Stage: Dilation of the cervix occurs as contractions begin. This stage can last several hours.
- Second Stage: The baby is pushed through the birth canal and delivered. This stage is often referred to as the “pushing” stage.
- Third Stage: Delivery of the placenta, which occurs after the baby is born.
17.7 FRATERNAL TWINS (Dizygotic Twins)
Fraternal twins are the result of the fertilization of two separate eggs by two separate sperm cells during the same menstrual cycle.
CHARACTERISTICS
- Fraternal twins share about 50% of their genetic material, similar to regular siblings.
- They can be of the same sex or different sexes.
17.8. IDENTICAL TWINS (Monozygotic Twins)
Identical twins are formed when a single fertilised egg (zygote) splits into two embryos during the early stages of development.
CHARACTERISTICS
- Identical twins share 100% of their genetic material, making them genetically identical.
- They are always of the same sex and often have very similar physical traits.
17.9. ADAPTIVE FEATURES OF THE EMBRYO(FOETUS)
- Placenta: The placenta establishes an intimate connection between the embryo and the mother.
- Yolk Sac: The yolk sac provides initial nourishment before the placenta is fully functional.
- Amniotic Sac: The embryo is surrounded by the amniotic sac filled with amniotic fluid, which cushions the embryo, protects it from physical shocks, and maintains a stable temperature.
- Chorion: This outer membrane helps in gas exchange and contributes to the formation of the placenta.
- Umbilical cord: It helps to attach the embryo to the placenta.
- Allantois: It aids respiration and excretion in the developing embryo.
17.10. VIVIPARITY
Viviparity is a mode of reproduction in which embryos develop inside the body of the mother, leading to live birth.
CHARACTERISTICS OF VIVIPAROUS ANIMALS
- The developing embryo receives nutrients directly from the mother through a placenta (in mammals).
- This method provides a more stable environment for the developing young and allows for greater parental care.
VIVIPAROUS ANIMALS : Most mammals, including humans, are viviparous. Some reptiles and fish also exhibit viviparity.
17.11. OVIPARITY
Oviparity is a mode of reproduction in which eggs are laid outside the mother’s body, and the embryos develop outside after fertilisation.
CHARACTERISTICS OF OVIPAROUS ANIMALS
- The eggs contain all the nutrients needed for the developing embryo.
- The young hatch from the eggs after a certain period, which can vary depending on the species and environmental conditions.
OVIPAROUS ANIMALS: Many birds, reptiles, amphibians, and most fish are oviparous.
17.12. TYPES OF REPRODUCTIVE CYCLE
- Estrous Cycle: The reproductive cycle in female mammals, which includes phases like estrus (heat) when the female is receptive to mating.
- Gestation: The period of development of the embryo/foetus inside the uterus, varying significantly among different mammal species.
17.13. SOME ORGANISMS AND THEIR FERTILIZATION TYPE
- Fish: Mostly external fertilisation; lay eggs in water.- Some species exhibit parental care.
- Amphibians: Typically external fertilisation; eggs laid in water.-Undergo metamorphosis (e.g., tadpole to frog).
- Reptiles: Mostly internal fertilisation; lay eggs on land-Some exhibit live birth (e.g., certain snakes).
- Birds: Internal fertilisation; lay hard-shelled eggs.High parental care; incubate eggs until hatching.
- Mammals: Internal fertilisation; most give live birth.-Extended parental care; young are nourished through milk.
DTW Tutorials Study Resource Links;
First of All to obtain high JAMB &WAEC Scores, YOU HAVE TO Practice! Practice!! Practice!!
Use DTW JAMB & WAEC 2025 CBT Practice App!!!
– GET DTW TUTORIALS JAMB & WAEC 2025 CBT EXAM PRACTICE APP for all Subjects with over 31,000 Past Questions and Correct Solutions to Practice with offline! (Activation cost is N4000 for 1 year) Download Links Below for Mobile Phones & Laptop Computer;
DTW TUTORIALS JAMB 2025 APP For MOBILE Phone Direct Download link;
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.iafsawii.dtw.jamb
DTW TUTORIALS JAMB 2025 APP For DESKTOP Laptop Computer Direct Download link; https://drive.google.com/file/d/1iIHBoWjEeJeCFyTO9nt-9kAveH2FqjrT/view?usp=sharing
Download Links for WAEC 2025 App;
JAMB RESOURCE LINKS BELOW;
– JAMB Past Questions Solved Playlists on Math, Phy, Chem; https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLLgYU6fS5143-p4dfWIFL7keuB1SBgT2b
– THE LEKKI HEADMASTER – Summary, Questions And Answers (JAMB 2025 NOVEL); https://dtwtutorials.com/the-lekki-headmaster-jamb-2025-novel-summary-questions-and-answers-pdf-download/
– JAMB 2025 Recommended Text Books – https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-recommended-text-books-for-all-subjects/
– JAMB 2025 Syllabus all Subjects – https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-syllabus-free-download/
– JAMB 2025 Syllabus in 30 Days Timetable Challenge by DTW Tutorials for Science, Art & Commercial Subject Combinations – Cover Your JAMB Syllabus in 30 Days Challenge; https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-syllabus-in-30-days-timetable-challenge-by-dtw-tutorials-cover-your-jamb-syllabus-in-30-days-challenge/
– How to Manage Your Jamb Exam Time for High Scores; https://youtu.be/Tp4Va8haib8
– Physics Notes and Questions on All topics; https://dtwtutorials.com/category/tutorials/physics-tutorials/
– Chemistry Notes and Questions on All topics; https://dtwtutorials.com/category/tutorials/chemistry/
– How to Read, Understand and Remember Always- https://youtu.be/kL8BpRePudA
– How to Cover Your JAMB Syllabus Fast in 30 Days!!; https://youtu.be/RVgyn01Ptd0
– What to do a night before your Jamb Exam (+Exam Prayers); https://youtu.be/njbAx4Oz5Rw
– How to Manage Your Jamb Exam Time for High Scores; https://youtu.be/Tp4Va8haib8
– Overcoming Exam Fear/Anxiety– https://youtu.be/Uvf81rvd0ls
You can also join our online groups below for instant JAMB 2025 Updates;
Join DTW JAMB 2025 Intensive Tutorials Study Groups on Facebook, Telegram and WhatsApp Group;
Facebook Group – https://web.facebook.com/groups/dtwtutorialsgroup/
WhatsApp Group – https://chat.whatsapp.com/E8pprCQYtahKfpQN9UB0aU
Telegram Group – https://t.me/+AcXfhJPSIiI2ZTY0
WhatsApp Channel – https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029VaAWvTmDDmFT9o25dV3u
DTW JAMB 2025 Intensive Online Lessons/Tutorials
Online JAMB 2025 Tutorials – Your Path to Jamb Success!
Are you preparing for the JAMB 2025 Exam and aiming for excellence? Look no further than Online Jamb Tutorial by DTW Consult. We’re dedicated to helping you ace your Jamb with confidence.
- Why Choose DTW Online JAMB Intensive Tutorials?
• Engaging, Clear and Interactive Online Lectures
• Completion of JAMB Syllabus
• Weekly Quiz Assessments
• Continuous Brainstorming and Competitions
• Membership in an Active Learning Community
• Consistent Solving of JAMB Past Questions-
• Expert Jamb Instructors
• Comprehensive Study Materials - All Classes are Recorded!! In case you miss any class, and when you join us you will have access to all the previous class recorded videos!!!
• Subjects;
English
Physics
Chemistry
Biology
Math
Economics
Literature
Crs
Government
• Affordable Tuition – N7000 monthly (6pm – 10pm, Mon to Fri)
Lectures Ongoing! Register Now!!
Bank Details:
Account Name: DTW Consult
Account Number: 6414330770
Bank: Moniepoint
Amount – N7000
For easy payment and enrollment.
Proof of payment should be sent by WhatsApp.
Contact Us:
WhatsApp: 09085099582, 08038732879
Email: dtwconsultng@gmail.com
Take a step closer to your Jamb success with DTW Online Jamb 2025 Intensive Tutorials.
Let’s work together to unlock your full potential!

https://youtu.be/P7wtBH46ZMMnsive Tutorials. Let’s work together to unlock your full potential! #JambPrep #OnlineTutorial #DTWConsult #JambSuccess #jamb2025 #utme2025

No Comments