7.0 INTRODUCTION TO REPRODUCTION
Reproduction is the biological process by which organisms produce new individuals of the same species. It is divided into two namely:
- Asexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction
7.1 ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION AND ITS TYPES
Asexual reproduction involves a single parent organism. Offspring of this reproduction, known as clones, are genetically identical to the parent. The mitotic cell division is involved in this process.
TYPES OF ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
- Binary Fission: Division of a single organism into two equal parts (e.g., bacteria).
- Budding: Formation of a new organism from a bud on the parent (e.g., yeast).
- Fragmentation: Breaking of the parent organism into fragments, each capable of growing into a new individual (e.g., starfish).
- Vegetative Propagation: A form of asexual reproduction in plants where new individuals arise from vegetative parts (e.g., tubers, runners).
7.2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Sexual reproduction involves two parent organisms (male and female). Offspring have genetic variation due to the combination of genetic material from both parents. The meiotic cell division is involved in this process.
Key processes involved in sexual reproduction include:
- Fertilization: Fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
This process can take the form of:
- External Fertilization: Occurs Outside the female’s body (e.g., in water). Common in aquatic animals like fish and amphibians. It involves the release of eggs and sperm into the environment.
- Internal Fertilization: Occurs inside the female’s body.Common in terrestrial animals (e.g., mammals, reptiles). It involves the transfer of sperm directly into the female reproductive tract.
- Development: The zygote undergoes cell division and differentiation to develop into a new organism.
7.3 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
Flowers are the reproductive structures of angiosperms.
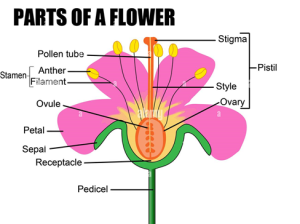
STRUCTURE OF A FLOWER
- Sepals: Protect the flower bud before it opens.
- Petals: Attract pollinators with their colour and fragrance.
- Stamens: Male reproductive organs, consisting of:
- Anther: Produces pollen grains (male gametes).
- Filament: Supports the anther.
- Carpels (Pistils): Female reproductive organs, consisting of:
- Ovary: Contains Ovules (female gametes).
- Style: Connects the ovary to the stigma.
- Stigma: Receives pollen during pollination.
7.4 FRUITS AND ITS CLASSIFICATION
A fruit is the mature ovary of a flowering plant, usually containing seeds.
It develops from the fertilized ovary of a flower and serves to protect the seeds and help in their dispersal. NB – Not all fruits are from fertilized ovary.
CLASSIFICATION OF FRUITS
- SIMPLE FRUITS: Develop from a single ovary of a single flower. Examples of simple fruits are apples, cherries, oranges etc. It can be further classified into:
- Fleshy Fruit: Have a soft and edible pericarp (e.g., apples, tomatoes).
- Dry Fruit: Have a hard or papery pericarp and can be either dehiscent (split open at maturity) or indehiscent (do not split open) (e.g., peas, nuts).
- AGGREGATE FRUITS: Form from multiple ovaries of a single flower. Each ovary develops into a small fruitlet, and they cluster together (e.g., strawberries, blackberries).
- COMPOSITE/MULTIPLE FRUITS: Develop from the ovaries of multiple flowers that are closely packed together. The individual fruits fuse together to form a single mass (e.g., pineapples, figs).
7.7 FRUIT STRUCTURE
- Exocarp: The outer layer of the fruit.
- Mesocarp: The fleshy middle layer.
- Endocarp: The innermost layer that surrounds the seed.
7.8 PLACENTATION
Placentation refers to the arrangement of ovules within the ovary of a flower. It plays a crucial role in the development of seeds.
TYPES OF PLACENTATION
- Marginal Placentation: Ovules are attached along the margin of a single carpel (e.g., Beans, copper, pride of Barbados).
- Axile Placentation: Ovules are attached to a central column in a compound ovary, with two or more carpels (e.g., tomatoes, oranges).
- Parietal Placentation: Ovules are attached to the inner wall of the ovary, and the ovary is usually one chamber (e.g., pawpaw, mustard).
- Free Central Placentation: Ovules are attached to a central column but are not separated by septa (e.g., dianthus, canna lily).
- Basal Placentation: Ovules are attached at the base of the ovary (e.g., sunflower).
7.9 POLLINATION AND ITS TYPES
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma.
TYPES OF POLLINATION
- Self-Pollination: Pollen from the same flower or another flower on the same plant fertilizes the ovule.
- Cross-Pollination: Pollen from one flower fertilizes the ovule of another flower, promoting genetic diversity. Pollinators include insects (bees, butterflies), birds, wind, and water.
7.10 AGENTS OF POLLINATION
INSECT-POLLINATED FLOWERS (Entomophilous Flowers) – Insects transfer pollen from the anthers of one flower to the stigma of another, facilitating cross-pollination.
CHARACTERISTICS OF INSECT POLLINATED FLOWERS
- Brightly coloured petals to attract insects.
- Strong, sweet fragrances to lure pollinators.
- Nectar production to provide a food source for insects.
STRUCTURE OF INSECT POLLINATED FLOWERS.
- Often have a landing platform for insects.
- Pollen is usually sticky or spiky to adhere to the bodies of insects.
Pollinators Of Entomophilous Flowers – Common pollinators include bees, butterflies, moths, and beetles.
ADVANTAGES OF INSECT POLLINATED FLOWERS
- Insect pollination often leads to higher seed set and genetic diversity due to cross-pollination.
- Flowers can be more specialized, leading to co-evolution with specific pollinators.
Examples Of Insect Pollinated Flowers – Flowers like sunflowers, orchids, and roses are typically insect pollinated.
WIND-POLLINATED FLOWERS (Anemophilous Flowers) – Pollen is dispersed by the wind, and the flowers rely on chance for pollen to land on the stigma of another flower.
CHARACTERISTICS OF WIND POLLINATED FLOWERS
- Usually lack bright colours and fragrances since they do not rely on visual or olfactory cues to attract pollinators.
- Often have small, inconspicuous flowers.
STRUCTURE OF WIND POLLINATED FLOWERS
- Pollen grains are lightweight and produced in large quantities to increase the chances of successful pollination.
- Flowers may have long, feathery stigmas to catch drifting pollen.
ADVANTAGES OF WIND POLLINATED FLOWERS
- Wind pollination can be more efficient in open areas where flowers are abundant.
- It does not depend on the presence of pollinators, making it reliable in various environmental conditions.
Examples Of Wind Pollinated Flowers – Common wind-pollinated plants include grasses, corn, and many trees like oaks and pines.
FERTILIZATION – After pollination, pollen grains germinate on the stigma, forming a pollen tube that grows down the style to the ovary. Fertilization occurs when the male gamete (sperm) travels through the pollen tube and fuses with the female gamete (ovule) in the ovary, forming a zygote. The zygote develops into an embryo, while the ovule develops into a seed.
7.11 GERMINATION AND ITS TYPES
Germination is the process by which a seed develops into a new plant. It begins when a seed absorbs water, swells, and breaks through its seed coat, leading to the growth of the embryo inside. The root (radicle) is usually the first part to emerge, followed by the shoot (plumule), which grows upward to form the stem and leaves.
TYPES OF GERMINATION
- Epigeal Germination: The cotyledons (seed leaves) emerge above the soil surface (e.g., beans).
- Hypogeal Germination: The cotyledons remain below the soil surface while the shoot emerges (e.g., peas).
CONDITIONS NECESSARY FOR GERMINATION
- Water – to activate enzymes and soften the seed coat.
- Oxygen – for respiration to release energy.
- Suitable temperature – for enzyme activity and growth.
7.12 SEED DEVELOPMENT
The ovary develops into a fruit, which protects the seeds and aids in their dispersal. Seeds, developed from the ovule, consist of:
- Seed Coat: Protects the seed.
- Embryo: The young plant that will develop.
- Endosperm: Provides nourishment to the developing embryo.
7.13 SEED DISPERSAL
Seed dispersal is the process by which seeds are spread away from the parent plant to reduce competition.
METHODS OF SEED DISPERSAL
- Wind Dispersal: Seeds are light weight and carried by the wind (e.g., dandelions).
- Animal Dispersal: Seeds are eaten and later excreted by animals (e.g., berries).
- Water Dispersal: Seeds float and are carried by water (e.g., coconuts).
- Explosion (Self-dispersal): Pods burst open and scatter seeds (e.g., pea, castor)
IMPORTANCE OF SEED DISPRSAL
- Reduces competition for light, water, and nutrients.
- Helps plants colonize new environments.
- Increases the chances of survival and reproduction.
DTW Tutorials Study Resource Links;
First of All to obtain high JAMB &WAEC Scores, YOU HAVE TO Practice! Practice!! Practice!!
Use DTW JAMB & WAEC 2025 CBT Practice App!!!
– GET DTW TUTORIALS JAMB & WAEC 2025 CBT EXAM PRACTICE APP for all Subjects with over 31,000 Past Questions and Correct Solutions to Practice with offline! (Activation cost is N4000 for 1 year) Download Links Below for Mobile Phones & Laptop Computer;
DTW TUTORIALS JAMB 2025 APP For MOBILE Phone Direct Download link;
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.iafsawii.dtw.jamb
DTW TUTORIALS JAMB 2025 APP For DESKTOP Laptop Computer Direct Download link; https://drive.google.com/file/d/1iIHBoWjEeJeCFyTO9nt-9kAveH2FqjrT/view?usp=sharing
Download Links for WAEC 2025 App;
JAMB RESOURCE LINKS BELOW;
– JAMB Past Questions Solved Playlists on Math, Phy, Chem; https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLLgYU6fS5143-p4dfWIFL7keuB1SBgT2b
– THE LEKKI HEADMASTER – Summary, Questions And Answers (JAMB 2025 NOVEL); https://dtwtutorials.com/the-lekki-headmaster-jamb-2025-novel-summary-questions-and-answers-pdf-download/
– JAMB 2025 Recommended Text Books – https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-recommended-text-books-for-all-subjects/
– JAMB 2025 Syllabus all Subjects – https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-syllabus-free-download/
– JAMB 2025 Syllabus in 30 Days Timetable Challenge by DTW Tutorials for Science, Art & Commercial Subject Combinations – Cover Your JAMB Syllabus in 30 Days Challenge; https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-syllabus-in-30-days-timetable-challenge-by-dtw-tutorials-cover-your-jamb-syllabus-in-30-days-challenge/
– How to Manage Your Jamb Exam Time for High Scores; https://youtu.be/Tp4Va8haib8
– Physics Notes and Questions on All topics; https://dtwtutorials.com/category/tutorials/physics-tutorials/
– Chemistry Notes and Questions on All topics; https://dtwtutorials.com/category/tutorials/chemistry/
– How to Read, Understand and Remember Always- https://youtu.be/kL8BpRePudA
– How to Cover Your JAMB Syllabus Fast in 30 Days!!; https://youtu.be/RVgyn01Ptd0
– What to do a night before your Jamb Exam (+Exam Prayers); https://youtu.be/njbAx4Oz5Rw
– How to Manage Your Jamb Exam Time for High Scores; https://youtu.be/Tp4Va8haib8
– Overcoming Exam Fear/Anxiety– https://youtu.be/Uvf81rvd0ls
You can also join our online groups below for instant JAMB 2025 Updates;
Join DTW JAMB 2025 Intensive Tutorials Study Groups on Facebook, Telegram and WhatsApp Group;
Facebook Group – https://web.facebook.com/groups/dtwtutorialsgroup/
WhatsApp Group – https://chat.whatsapp.com/E8pprCQYtahKfpQN9UB0aU
Telegram Group – https://t.me/+AcXfhJPSIiI2ZTY0
WhatsApp Channel – https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029VaAWvTmDDmFT9o25dV3u
DTW JAMB 2025 Intensive Online Lessons/Tutorials
Online JAMB 2025 Tutorials – Your Path to Jamb Success!
Are you preparing for the JAMB 2025 Exam and aiming for excellence? Look no further than Online Jamb Tutorial by DTW Consult. We’re dedicated to helping you ace your Jamb with confidence.
- Why Choose DTW Online JAMB Intensive Tutorials?
• Engaging, Clear and Interactive Online Lectures
• Completion of JAMB Syllabus
• Weekly Quiz Assessments
• Continuous Brainstorming and Competitions
• Membership in an Active Learning Community
• Consistent Solving of JAMB Past Questions-
• Expert Jamb Instructors
• Comprehensive Study Materials - All Classes are Recorded!! In case you miss any class, and when you join us you will have access to all the previous class recorded videos!!!
• Subjects;
English
Physics
Chemistry
Biology
Math
Economics
Literature
Crs
Government
• Affordable Tuition – N7000 monthly (6pm – 10pm, Mon to Fri)
Lectures Ongoing! Register Now!!
Bank Details:
Account Name: DTW Consult
Account Number: 6414330770
Bank: Moniepoint
Amount – N7000
For easy payment and enrollment.
Proof of payment should be sent by WhatsApp.
Contact Us:
WhatsApp: 09085099582, 08038732879
Email: dtwconsultng@gmail.com
Take a step closer to your Jamb success with DTW Online Jamb 2025 Intensive Tutorials.
Let’s work together to unlock your full potential!

https://youtu.be/P7wtBH46ZMMnsive Tutorials. Let’s work together to unlock your full potential! #JambPrep #OnlineTutorial #DTWConsult #JambSuccess #jamb2025 #utme2025

No Comments