1.0. INTRODUCTION TO LIVING ORGANISMS
Living organisms are all forms of life that carry out basic life processes. They include plants, animals, fungi, protists, and bacteria. These organisms are made up of cells, which are the basic units of life. They interact with their environment, adapt to changes, and maintain internal balance (homeostasis). Understanding living organisms is key to studying biology, the science of life.
1.1 CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS
MOVEMENT – Ability of an organism to move its whole body or part of its body from one place to another.
RESPIRATION – Process of releasing energy from food.
NUTRITION – Taking in food for energy and growth.
IRRITABILITY/SENSITIVITY – Response to stimuli.
GROWTH – Irreversible increase in size,dry mass and complexity.
EXCRETION – Removal of metabolic waste from the body.
REPRODUCTION – Ability to produce.
DEATH – End of life processes.
ADAPTATION – Ability to adjust to the environment.
COMPETITION – Ability of organisms to struggle for the necessities of life in order to survive in their various environments.
The characteristics of living things can be easily remembered with the acronym MR NIGER DAC.
1.2 CLASSIFICATIONS OF LIVING THINGS
Classification of living things began with Aristotle, later improved by Carolus Linnaeus in 1758 using a formal taxonomic system. The father of taxonomy, Carolus Linnaeus, developed the modern system of naming and classifying organisms called Binomial Nomenclature.
Living things were classified based on:
- Kingdom
- Phylum (for animals) – Division (for plants)
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
BASED ON KINGDOMS
- Kingdom Monera (e.g., bacteria)
- Kingdom Protista (e.g., amoeba)
- Kingdom Fungi (e.g., mushrooms)
- Kingdom Plantae (e.g., flowering plants)
— Under this classification, they are further divided into;
- Bryophytes – Includes mosses and liverworts. They lack true roots, stems and leaves and reproduce via spores.
- Pteridophytes – They are divided into two;
- Gymnosperms – Seed-producing plants that do not produce flowers or fruits (e.g., conifers like pine trees).
- Angiosperms – Flowering plants that produce seeds enclosed in fruits. They are divided into:
- Monocotyledons – One seed leaf (e.g. grasses, lilies, maize, cereals).
- Dicotyledons – Two seed leaves (e.g., roses, sunflowers, bean, cowpea).
- Thallophyta (e.g,green,brown,red algae).
- Tracheophyta (e.g vascular plants).
● Kingdom Animalia (e.g., mammals, birds).
1.3 INTRODUCTION TO CELL
A cell is defined as the smallest, basic unit of life that is responsible for all of life’s processes. It can also be defined as a mass of cytoplasm that is bound externally by a cell membrane.
Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane. A living thing, whether made of one cell (like bacteria) or many cells (like a human), is called an organism.
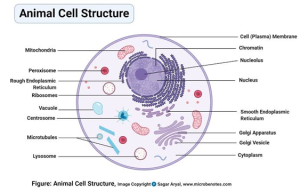
1.4 CELL STRUCTURES AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
Cell structures are the different parts or components within a cell that carry out specific functions necessary for the cell’s survival and proper functioning. These structures are also known as Cell Organelles.
They include:
- Cell Membrane – Plays a great role in selective Absorption of materials and protection of the cell.
- Nucleus – Contains hereditary information as it houses the DNA.
- Mitochondria – Powerhouse of the cell,where respiration occurs.
- Chloroplasts – Site of photosynthesis in plant cells.
- Cell wall – It provides protection,shape and mechanical support for the cell.
- Lysosomes – They are sites for respiratory enzymes.
- Ribosomes – They are responsible for protein synthesis.
- Centrioles – They are important in cell division and also serve as the basal body.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum – They aid the transport of materials within the cytoplasm.
- Vacuole – It contains cell sap which acts as an osmoregulator to remove excess water.
- Starch Granules – They store starch for the cell.
- Golgi bodies – They function in synthesis and packaging.
- Nucleolus – They produce ribosomes for protein synthesis.
1.5 FORMS IN WHICH LIVING CELL EXIST
- Single or Free Living Organisms – These are organisms that exist independently and are composed of a single cell. Examples include amoeba, paramecium.
- Filamentous Forms – Some organisms exist in long, thread-like structures called filaments e.g. spirogyra.
- Colony Forms – In this form, groups of cells live together but can function independently. Examples include volvox that form colonies.
1.6 UNICELLULAR & MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS
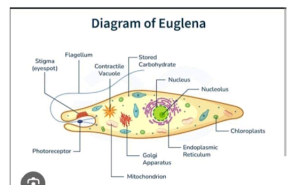
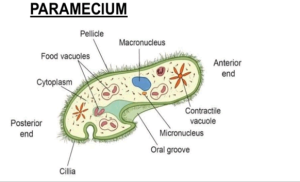
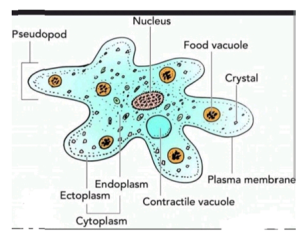
UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS – These are made of a single cell that carries out all life processes. Examples: Bacteria, Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena
MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS – These consist of many specialized cells working together. Examples: Plants, animals, humans etc. in multicellular organisms, some of these specialized cells include:
- Red blood cells (carry oxygen).
- Nerve cells (transmit signals).
- Muscle cells (contract and enable movement).
- White blood cells (defend against disease) etc.
MOVEMENT MECHANISMS IN UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS
- Flagella – Long, whip-like structures that propel organisms (e.g., euglena).
- Cilia – Short, hair-like projections that beat in waves for movement (e.g., paramecium).
- Pseudopodia – Temporary extensions of the cell that allow crawling and feeding (e.g., amoeba).
1.7 PLANT AND ANIMAL CELL
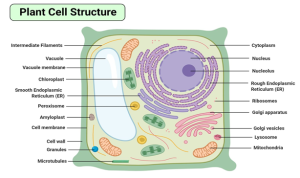
CHARACTERISTICS OF PLANT CELLS
- Cell Wall – Plant cells have a rigid cell wall made of cellulose that provides structure and support.
- Chloroplasts – These organelles contain chlorophyll and are responsible for photosynthesis, allowing plants to convert sunlight into energy.
- Large Central Vacuole – Plant cells typically have a large central vacuole that stores water, nutrients, and waste products, helping maintain turgor pressure.
- Definite Shape – Plant cells usually have a fixed, rectangular shape due to the presence of the cell wall.
CHARACTERISTICS OF ANIMAL CELLS
- No Cell Wall – Animal cells do not have a cell wall; instead, they have a flexible plasma membrane that allows for a variety of shapes.
- Centrioles – These structures are involved in cell division and help organise the mitotic spindle.
- Lysosomes – Animal cells contain lysosomes that contain digestive enzymes for breaking down waste materials and cellular debris.
- Small Vacuoles – Animal cells have smaller vacuoles compared to plant cells, which are used for storage and transport.
- Irregular Shape – Animal cells can vary in shape and size, often appearing round or irregular.
1.8 BRIEF HISTORY OF CELL
- 1665 – Robert Hooke (Father of Cell) – First person to observe cells. He looked at cork under a microscope and saw tiny box-like structures, which he called “cells.”
- 1674 – Anton van Leeuwenhoek – Improved the microscope and became the first to observe living cells (like bacteria and protozoa), which he called “animalcules.”
- 1838 – Matthias Schleiden – A botanist who concluded that all plants are made of cells.
- 1839 – Theodor Schwann – A zoologist who stated that all animals are also made of cells. Together with Schleiden, they proposed the early version of the cell theory.
- 1855 – Rudolf Virchow – Added the third part of the cell theory: “All cells arise from pre-existing cells.”
CELL THEORY
- All living things are made up of cells.
- The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms.
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
1.9 LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION
Level of organization refers to the hierarchy of complex biological structures and systems that make up living organisms. It shows how simple components combine to form more complex systems.
In biology, the common levels of organization are:
- Cell – The basic unit of life.
- Tissue – A group of similar cells working together.
- Organ – Different tissues working together to perform a function.
- System – A group of organs that work together (e.g., digestive system).
- Organism – A complete living being.
DTW Tutorials Study Resource Links;
First of All to obtain high JAMB &WAEC Scores, YOU HAVE TO Practice! Practice!! Practice!!
Use DTW JAMB & WAEC 2025 CBT Practice App!!!
– GET DTW TUTORIALS JAMB & WAEC 2025 CBT EXAM PRACTICE APP for all Subjects with over 31,000 Past Questions and Correct Solutions to Practice with offline! (Activation cost is N4000 for 1 year) Download Links Below for Mobile Phones & Laptop Computer;
DTW TUTORIALS JAMB 2025 APP For MOBILE Phone Direct Download link;
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.iafsawii.dtw.jamb
DTW TUTORIALS JAMB 2025 APP For DESKTOP Laptop Computer Direct Download link; https://drive.google.com/file/d/1iIHBoWjEeJeCFyTO9nt-9kAveH2FqjrT/view?usp=sharing
Download Links for WAEC 2025 App;
JAMB RESOURCE LINKS BELOW;
– JAMB Past Questions Solved Playlists on Math, Phy, Chem; https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLLgYU6fS5143-p4dfWIFL7keuB1SBgT2b
– THE LEKKI HEADMASTER – Summary, Questions And Answers (JAMB 2025 NOVEL); https://dtwtutorials.com/the-lekki-headmaster-jamb-2025-novel-summary-questions-and-answers-pdf-download/
– JAMB 2025 Recommended Text Books – https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-recommended-text-books-for-all-subjects/
– JAMB 2025 Syllabus all Subjects – https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-syllabus-free-download/
– JAMB 2025 Syllabus in 30 Days Timetable Challenge by DTW Tutorials for Science, Art & Commercial Subject Combinations – Cover Your JAMB Syllabus in 30 Days Challenge; https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-syllabus-in-30-days-timetable-challenge-by-dtw-tutorials-cover-your-jamb-syllabus-in-30-days-challenge/
– How to Manage Your Jamb Exam Time for High Scores; https://youtu.be/Tp4Va8haib8
– Physics Notes and Questions on All topics; https://dtwtutorials.com/category/tutorials/physics-tutorials/
– Chemistry Notes and Questions on All topics; https://dtwtutorials.com/category/tutorials/chemistry/
– How to Read, Understand and Remember Always- https://youtu.be/kL8BpRePudA
– How to Cover Your JAMB Syllabus Fast in 30 Days!!; https://youtu.be/RVgyn01Ptd0
– What to do a night before your Jamb Exam (+Exam Prayers); https://youtu.be/njbAx4Oz5Rw
– How to Manage Your Jamb Exam Time for High Scores; https://youtu.be/Tp4Va8haib8
– Overcoming Exam Fear/Anxiety– https://youtu.be/Uvf81rvd0ls
You can also join our online groups below for instant JAMB 2025 Updates;
Join DTW JAMB 2025 Intensive Tutorials Study Groups on Facebook, Telegram and WhatsApp Group;
Facebook Group – https://web.facebook.com/groups/dtwtutorialsgroup/
WhatsApp Group – https://chat.whatsapp.com/E8pprCQYtahKfpQN9UB0aU
Telegram Group – https://t.me/+AcXfhJPSIiI2ZTY0
WhatsApp Channel – https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029VaAWvTmDDmFT9o25dV3u
DTW JAMB 2025 Intensive Online Lessons/Tutorials
Online JAMB 2025 Tutorials – Your Path to Jamb Success!
Are you preparing for the JAMB 2025 Exam and aiming for excellence? Look no further than Online Jamb Tutorial by DTW Consult. We’re dedicated to helping you ace your Jamb with confidence.
- Why Choose DTW Online JAMB Intensive Tutorials?
• Engaging, Clear and Interactive Online Lectures
• Completion of JAMB Syllabus
• Weekly Quiz Assessments
• Continuous Brainstorming and Competitions
• Membership in an Active Learning Community
• Consistent Solving of JAMB Past Questions-
• Expert Jamb Instructors
• Comprehensive Study Materials - All Classes are Recorded!! In case you miss any class, and when you join us you will have access to all the previous class recorded videos!!!
• Subjects;
English
Physics
Chemistry
Biology
Math
Economics
Literature
Crs
Government
• Affordable Tuition – N7000 monthly (6pm – 10pm, Mon to Fri)
Lectures Ongoing! Register Now!!
Bank Details:
Account Name: DTW Consult
Account Number: 6414330770
Bank: Moniepoint
Amount – N7000
For easy payment and enrollment.
Proof of payment should be sent by WhatsApp.
Contact Us:
WhatsApp: 09085099582, 08038732879
Email: dtwconsultng@gmail.com
Take a step closer to your Jamb success with DTW Online Jamb 2025 Intensive Tutorials.
Let’s work together to unlock your full potential!

https://youtu.be/P7wtBH46ZMMnsive Tutorials. Let’s work together to unlock your full potential! #JambPrep #OnlineTutorial #DTWConsult #JambSuccess #jamb2025 #utme2025

No Comments