22.0 MODELS OF THE ATOM AND THEIR LIMITATIONS
- Dalton’s Model: Atoms are indivisible; does not explain isotopes.
- Thomson’s Model: Plum pudding model; fails to explain atomic structure.
- Rutherford’s Model: Nucleus at centre; does not explain electron orbits.
- Bohr’s Model: Electrons in fixed orbits; limited to hydrogen-like atoms.
22.1 DALTON’S ATOMIC THEORY
- All matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atom.
- Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties.
- Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed.
- Atoms of different elements can combine in simple whole number ratios to form chemical compounds.
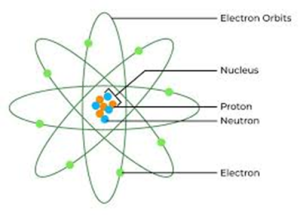
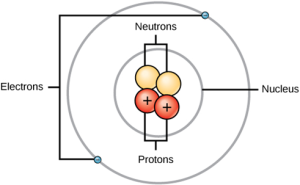
22.2 BASIC COMPONENTS OF ATOM
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the nucleus. Each proton has a charge of +1e and a mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu).
- Neutrons: Neutral particles also located in the nucleus. Neutrons have no charge and a mass like that of protons (approximately 1 amu).
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus. Each electron has a charge of -1e and a mass of about 1/1836 amu, which is negligible compared to protons and neutrons.
Nucleus: The nucleus is the central part of the atom, containing protons and neutrons.
22.3 ATOMIC NUMBER AND MASS NUMBER
- Atomic Number (Z): The number of protons in the nucleus, which defines the element. The proton/atomic number determines the identity of an element.
- Mass Number (A): The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus:
A = Z + N (where N is the number of neutrons).
ISOTOPES: Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes have the same chemical properties but different physical properties (e.g., different mass).
Example: Carbon-12 and Carbon-14.
22.4 DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ENERGY LEVELS AND SPECTRA
- Electrons occupy discrete energy levels.
- Energy transitions result in emission or absorption spectra.
22.5 THERMIONIC EMISSION
It is the process by which electrons are emitted from a material (usually a metal) when it is heated to a high temperature.
MECHANISM: At elevated temperatures, some electrons gain enough thermal energy to overcome the work function (the minimum energy needed to remove an electron from the surface).
APPLICATIONS OF THERMIONIC EMISSIONS: Used in vacuum tubes, cathode ray tubes, and electron guns in devices like oscilloscopes.
22.6 PHOTOELECTRIC EMISSION
It is the phenomenon where electrons are emitted from a material when it absorbs light or electromagnetic radiation.
MECHANISM: When photons strike the surface of a material, they transfer energy to electrons. If the energy of the photons exceeds the work function, electrons are emitted.
KEY EQUATION: Einstein’s equation for the photoelectric effect is given by:
E = hf
Where E is the energy of the emitted electron,
h is Planck’s constant (6.63 x 10-34 J·s), and
f is the frequency of the incident light.
APPLICATIONS OF PHOTOELECTRIC EMISSION: Used in solar cells, photodetectors, and photoelectric sensors.
WORK FUNCTION (WΦ): The work function of a material is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from that material.
- The energy of the emitted electron depends on the frequency of the incident light and the work function of the material.
STOPPING POTENTIAL: Stopping potential (Vs) is the minimum voltage needed to stop the most energetic photoelectrons emitted from a material.
It is related to the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons by the equation:
eVs = E
Where e: Charge of the electron (1.6 x 10-19 C),
Vs: Stopping potential in volts,
E: Kinetic energy of the emitted electron.
22.7 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN EINSTEIN’S EQUATION AND STOPPING POTENTIAL
The stopping potential can be derived from Einstein’s equation by setting the kinetic energy equal to eVs.
Thus, we can express the stopping potential as:
Vs = (hf – Wφ) / e
BINDING ENERGY: Energy required to separate nucleons in a nucleus.
MASS DEFECT: Difference between mass of nucleus and sum of individual nucleons.
22.8 RADIOACTIVITY
Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of particles or radiation from an unstable atomic nucleus.
TYPES OF RADIATION
- Alpha Radiation (α): Consists of helium nuclei (2 protons and 2 neutrons); positively charged and has low penetration power (can be stopped by paper).
- Beta Radiation (β): Consists of high-energy electrons or positrons; negatively charged (beta-minus) or positively charged (beta-plus); moderate penetration power (can be stopped by aluminum).
- Gamma Radiation (γ): High-energy electromagnetic radiation; no charge and very high penetration power (requires thick lead or concrete to stop).
RADIOACTIVE DECAY: Radioactive decay is a random process where unstable nuclei lose energy by emitting radiation. Decay can be described by the decay constant (λ) and half-life (T₁/₂).
HALF-LIFE: it is the time taken for half of the radioactive substance to decay.
RADIOACTIVITY-DECAY LAW: The number of radioactive nuclei remaining after time t is given by:
N(t) = N₀ e(-λt)
Where N₀ is the initial quantity,
λ is the decay constant, and
t is time.
Half-life can be calculated using:
T₁/₂ = ln(2) / λ.
APPLICATIONS OF RADIOACTIVITY
- Used in medical treatments (e.g., cancer radiotherapy).
- Used in radiography for imaging and inspection. iii)Used in smoke detectors and carbon dating.
DETECTION OF RADIATION – Radioactivity can be detected using instruments such as Geiger counters, scintillation counters, and ionisation chambers.
22.9 NUCLEAR REACTION
A nuclear reaction is an interaction between two nuclear particles or two nuclei that results in the formation of new nuclei different from the original ones. It involves the collision and separation of particles or nuclei, resulting in elastic scattering or inelastic collisions.
NUCLEAR ENERGY: Nuclear energy is the energy released during nuclear reactions, particularly through processes such as nuclear fission and nuclear fusion.
TYPES OF NUCLEAR REACTIONS
- Nuclear Fission: This is the process where a heavy nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei, along with the release of a significant amount of energy, neutrons, and gamma radiation.
- Nuclear Fusion: This is the process where two light atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing energy in the process.
22.10 DUALITY OF MATTER
Matter exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties.
WAVE-PARTICLE DUALITY: Matter behaves as both waves and particles.
DE BROGLIE WAVELENGTH: λ = h/p (where h = Planck’s constant, p = momentum).
HEISENBERG’S UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE: It states that certain pairs of physical properties, like position (x) and momentum (p), cannot be simultaneously known to arbitrary precision. The more accurately one property is known, the less accurately the other can be known.
It is given by the formula: Δx · Δp ≥ h/(4π) (uncertainty in position and momentum)
DTW Tutorials Study Resource Links;
First of All to obtain high JAMB &WAEC Scores, YOU HAVE TO Practice! Practice!! Practice!!
Use DTW JAMB & WAEC 2025 CBT Practice App!!!
– GET DTW TUTORIALS JAMB & WAEC 2025 CBT EXAM PRACTICE APP for all Subjects with over 31,000 Past Questions and Correct Solutions to Practice with offline! (Activation cost is N4000 for 1 year) Download Links Below for Mobile Phones & Laptop Computer;
DTW TUTORIALS JAMB 2025 APP For MOBILE Phone Direct Download link;
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.iafsawii.dtw.jamb
DTW TUTORIALS JAMB 2025 APP For DESKTOP Laptop Computer Direct Download link; https://drive.google.com/file/d/1iIHBoWjEeJeCFyTO9nt-9kAveH2FqjrT/view?usp=sharing
Download Links for WAEC 2025 App;
JAMB RESOURCE LINKS BELOW;
– JAMB Past Questions Solved Playlists on Math, Phy, Chem; https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLLgYU6fS5143-p4dfWIFL7keuB1SBgT2b
– THE LEKKI HEADMASTER – Summary, Questions And Answers (JAMB 2025 NOVEL); https://dtwtutorials.com/the-lekki-headmaster-jamb-2025-novel-summary-questions-and-answers-pdf-download/
– JAMB 2025 Recommended Text Books – https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-recommended-text-books-for-all-subjects/
– JAMB 2025 Syllabus all Subjects – https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-syllabus-free-download/
– JAMB 2025 Syllabus in 30 Days Timetable Challenge by DTW Tutorials for Science, Art & Commercial Subject Combinations – Cover Your JAMB Syllabus in 30 Days Challenge; https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-syllabus-in-30-days-timetable-challenge-by-dtw-tutorials-cover-your-jamb-syllabus-in-30-days-challenge/
– How to Manage Your Jamb Exam Time for High Scores; https://youtu.be/Tp4Va8haib8
– Physics Notes and Questions on All topics; https://dtwtutorials.com/category/tutorials/physics-tutorials/
– Chemistry Notes and Questions on All topics; https://dtwtutorials.com/category/tutorials/chemistry/
– How to Read, Understand and Remember Always- https://youtu.be/kL8BpRePudA
– How to Cover Your JAMB Syllabus Fast in 30 Days!!; https://youtu.be/RVgyn01Ptd0
– What to do a night before your Jamb Exam (+Exam Prayers); https://youtu.be/njbAx4Oz5Rw
– How to Manage Your Jamb Exam Time for High Scores; https://youtu.be/Tp4Va8haib8
– Overcoming Exam Fear/Anxiety– https://youtu.be/Uvf81rvd0ls
You can also join our online groups below for instant JAMB 2025 Updates;
Join DTW JAMB 2025 Intensive Tutorials Study Groups on Facebook, Telegram and WhatsApp Group;
Facebook Group – https://web.facebook.com/groups/dtwtutorialsgroup/
WhatsApp Group – https://chat.whatsapp.com/E8pprCQYtahKfpQN9UB0aU
Telegram Group – https://t.me/+AcXfhJPSIiI2ZTY0
WhatsApp Channel – https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029VaAWvTmDDmFT9o25dV3u
DTW JAMB 2025 Intensive Online Lessons/Tutorials
Online JAMB 2025 Tutorials – Your Path to Jamb Success!
Are you preparing for the JAMB 2025 Exam and aiming for excellence? Look no further than Online Jamb Tutorial by DTW Consult. We’re dedicated to helping you ace your Jamb with confidence.
- Why Choose DTW Online JAMB Intensive Tutorials?
• Engaging, Clear and Interactive Online Lectures
• Completion of JAMB Syllabus
• Weekly Quiz Assessments
• Continuous Brainstorming and Competitions
• Membership in an Active Learning Community
• Consistent Solving of JAMB Past Questions-
• Expert Jamb Instructors
• Comprehensive Study Materials - All Classes are Recorded!! In case you miss any class, and when you join us you will have access to all the previous class recorded videos!!!
• Subjects;
English
Physics
Chemistry
Biology
Math
Economics
Literature
Crs
Government
• Affordable Tuition – N7000 monthly (6pm – 10pm, Mon to Fri)
Lectures Ongoing! Register Now!!
Bank Details:
Account Name: DTW Consult
Account Number: 6414330770
Bank: Moniepoint
Amount – N7000
For easy payment and enrollment.
Proof of payment should be sent by WhatsApp.
Contact Us:
WhatsApp: 09085099582, 08038732879
Email: dtwconsultng@gmail.com
Take a step closer to your Jamb success with DTW Online Jamb 2025 Intensive Tutorials.
Let’s work together to unlock your full potential!

https://youtu.be/P7wtBH46ZMMnsive Tutorials. Let’s work together to unlock your full potential! #JambPrep #OnlineTutorial #DTWConsult #JambSuccess #jamb2025 #utme2025

No Comments