11.0 DEFINITION OF ELECTROLYSIS AND OTHER TERMS INVOLVED
ELECTROLYSIS – It can be defined as the chemical decomposition of a compound (electrolyte) into its component ions by the passage of electric current through a solution of that compound or the molten compound.
ELECTROLYTE – It is a compound which when molten or in aqueous solution will conduct electricity and decomposes by it. An electrolyte could be classified into three:
- Strong electrolyte e.g. NaCl, NaOH, HCl, HNO3 etc.
- Weak electrolyte e.g. ethanoic acid and its salts, NH3 solution etc.
- Non-electrolyte e.g. benzene, sugar, ethanol, trichloromethane etc.
ELECTRODE – It is a conductor in the form of wire, plates or rods, through which an electric current enters or leaves the electrolyte. It is divided into two; anode and cathode.
11.1 TYPES OF ELECTRIC CELL
- Electrolytic cell – A device used for electrolysis, consisting of an electrolyte, electrodes, and an external power source.
- Electrochemical cell – A device/cell that converts chemical energy to electrical energy. Examples include galvanic or voltaic cell.
| ELECTROLYTIC CELL | ELECTROCHEMICAL CELL | |
| 1 | Requires electric current. | Produces electricity. |
| 2 | Cathode is the negative electrode. | Cathode is the positive electrode. |
| 3 | Anode is the positive electrode. | Anode is the negative electrode. |
| 4 | Electrical energy is converted into chemical energy. | Chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. |
| 5 | Reaction is spontaneous. | Reaction is non-spontaneous. |
11.2 FARADAY’S LAW OF ELECTROLYSIS
1ST LAW – It states that the mass of a substance deposited at the electrode during electrolysis, is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte.
- Mass(M) = Z × Current(I) × Time(t)
- Z = Electrochemical equivalent (Z = R.A.M / CF; where F = 96500C)
- Faraday’s constant (F) represents the charge of one mole of electrons, approximately 96,500 C/mol. One faraday discharge one mole of univalent element, A+, while two moles of faraday discharges one mole of divalent element, B2+.
2ND LAW – It states that when the quantity of electricity is passed through different electrolytes, the number of moles of the elements deposited are inversely proportional to the charges on the ions of the elements.
11.3 FACTORS AFFECTING PREFERENTIAL DISCHARGE OF IONS IN ELECTROLYSIS
- Position of the ion in the electrochemical series.
- Concentration of the ion in the electrolyte.
- Nature of electrode used.
11.4 ELECTROLYSIS OF SOME SUBSTANCES
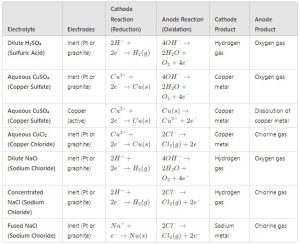
SUITABLE ELECTRODES FOR DIFFERENT ELECTROLYTES
- INERT ELECTRODES – Do not react with the electrolyte or products, such as platinum (Pt) or graphite (carbon). Suitable for electrolysis of solutions like NaCl, H₂SO₄, CuSO₄.
- ACTIVE ELECTRODES – Participate in the reaction, such as copper (Cu) electrodes in CuSO₄ electrolysis, where copper dissolves from the anode.
11.5 APPLICATIONS OF ELECTROLYSIS
- Purification of elements/metals e.g copper.
- Production of elements and compounds (Al, Na, O2, Cl2 and NaOH).
- Electroplating/coating of metals to prevent corrosion.
- Extraction of metals from ores (e.g., aluminum, copper).
- Electrolytic reduction of metals from their compounds.
11.5 REDOX SERIES
The redox series, also known as the electrochemical series or activity series, is a list of elements arranged according to their standard electrode potentials. It ranks elements (and their ions) based on how easily they ionize. The redox series are as follows: K, Ca, Na, Mg, Al, Zn, Fe, Sn, Pb, H, Cu, Hg, Ag, Au, and Pt.
- Elements at the top of the redox series (like potassium, calcium, and sodium) ionize easily by losing electrons, making them strong reducing agents. These elements are more reactive, have less standard electrode potential and are easily oxidized (acts as anode).
- Elements at the bottom of the series (like copper, silver, gold and platinum) ionize less easily. They tend to gain electrons, acting as oxidizing agents, have high standard electrode potential and are less reactive. These elements are easily reduced (acts as cathode).
11.6 HALF-CELL REACTIONS AND ELECTRODE POTENTIALS
A HALF-CELL REACTION represents either the oxidation or the reduction process that occurs in an electrochemical cell. There are two half-cells involved redox (reduction-oxidation) reaction. They are:
Oxidation half-cell reaction – In this reaction, an element loses electrons (oxidized). This occurs at the anode of the cell. Example: Zinc loses two electrons and becomes a zinc ion.
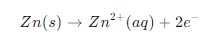
Reduction half-cell reaction – In this reaction, an element gains electron (reduced). This occurs at the cathode of the cell. Example: Copper ion gains two electrons and becomes copper metal.
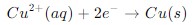
When combined, these two half-cell reactions form the complete redox reaction, where electrons are transferred from the anode to the cathode through an external circuit, generating electrical current.
THE STANDARD ELECTRODE POTENTIAL of metal ions/metal system is the potential difference set up between the metal and a one-molar solution of its ions at 25oC, (arbitrarily taking the standard electrode potential of the hydrogen ions/hydrogen gas system as zero volt).
The potential difference set up between a metal and its solution is called the electrode potential for that metal ions/metal system.
11.7 CORROSION AS AN ELECTROLYTIC PROCESS
Corrosion occurs when metals, especially iron, react with environmental factors (e.g., oxygen and moisture) in an electrolytic process, forming rust (Fe₂O₃·nH₂O). it could be prevented by using reactive metals like zinc for protection, applying paint to serve as shield, electroplating to create barriers, and using grease or oil to block moisture and prevent rust formation.
DTW Tutorials Study Resource Links;
First of All to obtain high JAMB &WAEC Scores, YOU HAVE TO Practice! Practice!! Practice!!
Use DTW JAMB & WAEC 2025 CBT Practice App!!!
– GET DTW TUTORIALS JAMB & WAEC 2025 CBT EXAM PRACTICE APP for all Subjects with over 31,000 Past Questions and Correct Solutions to Practice with offline! (Activation cost is N4000 for 1 year) Download Links Below for Mobile Phones & Laptop Computer;
DTW TUTORIALS JAMB 2025 APP For MOBILE Phone Direct Download link;
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.iafsawii.dtw.jamb
DTW TUTORIALS JAMB 2025 APP For DESKTOP Laptop Computer Direct Download link; https://drive.google.com/file/d/1iIHBoWjEeJeCFyTO9nt-9kAveH2FqjrT/view?usp=sharing
Download Links for WAEC 2025 App;
JAMB RESOURCE LINKS BELOW;
– JAMB Past Questions Solved Playlists on Math, Phy, Chem; https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLLgYU6fS5143-p4dfWIFL7keuB1SBgT2b
– THE LEKKI HEADMASTER – Summary, Questions And Answers (JAMB 2025 NOVEL); https://dtwtutorials.com/the-lekki-headmaster-jamb-2025-novel-summary-questions-and-answers-pdf-download/
– JAMB 2025 Recommended Text Books – https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-recommended-text-books-for-all-subjects/
– JAMB 2025 Syllabus all Subjects – https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-syllabus-free-download/
– JAMB 2025 Syllabus in 30 Days Timetable Challenge by DTW Tutorials for Science, Art & Commercial Subject Combinations – Cover Your JAMB Syllabus in 30 Days Challenge; https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-syllabus-in-30-days-timetable-challenge-by-dtw-tutorials-cover-your-jamb-syllabus-in-30-days-challenge/
– How to Manage Your Jamb Exam Time for High Scores; https://youtu.be/Tp4Va8haib8
– Physics Notes and Questions on All topics; https://dtwtutorials.com/category/tutorials/physics-tutorials/
– Chemistry Notes and Questions on All topics; https://dtwtutorials.com/category/tutorials/chemistry/
– How to Read, Understand and Remember Always- https://youtu.be/kL8BpRePudA
– How to Cover Your JAMB Syllabus Fast in 30 Days!!; https://youtu.be/RVgyn01Ptd0
– What to do a night before your Jamb Exam (+Exam Prayers); https://youtu.be/njbAx4Oz5Rw
– How to Manage Your Jamb Exam Time for High Scores; https://youtu.be/Tp4Va8haib8
– Overcoming Exam Fear/Anxiety– https://youtu.be/Uvf81rvd0ls
You can also join our online groups below for instant JAMB 2025 Updates;
Join DTW JAMB 2025 Intensive Tutorials Study Groups on Facebook, Telegram and WhatsApp Group;
Facebook Group – https://web.facebook.com/groups/dtwtutorialsgroup/
WhatsApp Group – https://chat.whatsapp.com/E8pprCQYtahKfpQN9UB0aU
Telegram Group – https://t.me/+AcXfhJPSIiI2ZTY0
WhatsApp Channel – https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029VaAWvTmDDmFT9o25dV3u
DTW JAMB 2025 Intensive Online Lessons/Tutorials
Online JAMB 2025 Tutorials – Your Path to Jamb Success!
Are you preparing for the JAMB 2025 Exam and aiming for excellence? Look no further than Online Jamb Tutorial by DTW Consult. We’re dedicated to helping you ace your Jamb with confidence.
- Why Choose DTW Online JAMB Intensive Tutorials?
• Engaging, Clear and Interactive Online Lectures
• Completion of JAMB Syllabus
• Weekly Quiz Assessments
• Continuous Brainstorming and Competitions
• Membership in an Active Learning Community
• Consistent Solving of JAMB Past Questions-
• Expert Jamb Instructors
• Comprehensive Study Materials - All Classes are Recorded!! In case you miss any class, and when you join us you will have access to all the previous class recorded videos!!!
• Subjects;
English
Physics
Chemistry
Biology
Math
Economics
Literature
Crs
Government
• Affordable Tuition – N7000 monthly (6pm – 10pm, Mon to Fri)
Lectures Ongoing! Register Now!!
Bank Details:
Account Name: DTW Consult
Account Number: 6414330770
Bank: Moniepoint
Amount – N7000
For easy payment and enrollment.
Proof of payment should be sent by WhatsApp.
Contact Us:
WhatsApp: 09085099582, 08038732879
Email: dtwconsultng@gmail.com
Take a step closer to your Jamb success with DTW Online Jamb 2025 Intensive Tutorials.
Let’s work together to unlock your full potential!

https://youtu.be/P7wtBH46ZMMnsive Tutorials. Let’s work together to unlock your full potential! #JambPrep #OnlineTutorial #DTWConsult #JambSuccess #jamb2025 #utme2025

No Comments