8.0 INTRODUCTION
Coordination and Control refers to the processes that allow an organism or system to regulate and direct its functions efficiently and harmoniously. In living organisms, survival depends on the ability to sense and respond to changes in the environment. These changes, called stimuli, can be internal or external.
Coordination ensures that different parts of an organism work together to produce a unified response to stimuli, while control involves regulating body activities to maintain stability and balance (homeostasis).
8.1 TYPES OF COORDINATION
- Nervous Coordination: Involves the nervous system, which includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
- Uses electrical impulses to transmit signals rapidly between different parts of the body.
- Enables quick responses to stimuli (e.g., reflex actions).
- Hormonal Coordination: Involves the endocrine system, which consists of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Examples include growth hormone, insulin, and adrenaline.
8.2 NERVOUS SYSTEM AND ITS TYPES
The nervous system is the body’s control and communication network. It is responsible for detecting changes in the environment (both inside and outside the body), processing that information, and coordinating appropriate responses.
The nervous system works closely with the endocrine system to regulate body functions, but it acts much faster, using electrical impulses rather than hormones.
TYPES OF NERVOUS SYSTEM
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Comprises the brain and spinal cord; processes information and coordinates responses.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Consists of all nerves that lies outside the brain and spinal cord. It connects the CNS to the rest of the body. It is further divided into two namely:
- Somatic Nervous System (SNS):
- Controls voluntary movements.
- Carries messages from the CNS to skeletal muscles (e.g., moving your arm).
- Also carries sensory information from the skin, joints, and muscles to the CNS.
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS):
- Controls involuntary activities (not under conscious control).
- Regulates internal organs like the heart, lungs, and digestive system.
- Has two main parts:
- Sympathetic Nervous System – Prepares the body for “fight or flight” (e.g., increases heartbeat).
- Parasympathetic Nervous System – Calms the body down after stress (“rest and digest”).
Neurons are the basic functional units of the nervous system, transmitting signals through electrical impulses.
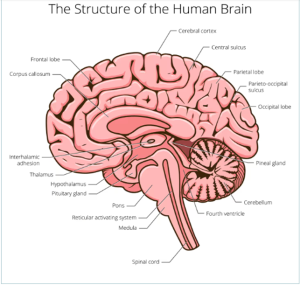
8.3 STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN
- Cerebrum: Largest part of the brain, control voluntary actions e.g, walking, singing. It is the seat of consciousness, intelligence, memory, learning.
- Cerebellum: Located under the cerebrum, coordinates voluntary movements like balance, and posture, Important for motor control and learning motor skills.
- Medulla Oblongata: Controls autonomic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
- Thalamus: Acts as a relay station for sensory information (except for smell) and directs it to the appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex for processing. It helps to experience sensation.
Hypothalamus: Regulates homeostasis by controlling body temperature, hunger, thirst, and circadian rhythms. Plays a crucial role in the endocrine system by influencing hormone release from the pituitary gland.
8.4 REFLEX ACTION
Reflex actions are automatic, rapid responses to stimuli that do not involve conscious thought.
EXAMPLES OF REFLEX ACTIONS
- Pulling your hand away from a hot object.
- Blinking when something comes close to your eyes.
- Sneezing when something irritates your nose.
- Knee-jerk response during a medical check-up.
8.5 TYPES OF NEURONS
- Sensory Neuron: Transmits the signal to the CNS.
- Inter-neuron: Processes the information in the CNS.
- Motor Neuron: Carries the response signal to the effector.
8.6 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
The endocrine system comprises glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. It is a control system in the body that uses hormones to regulate various functions such as growth, metabolism, development, mood, and reproduction.
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands that are released into the bloodstream.
Unlike the nervous system (which uses electrical signals), the endocrine system works more slowly, using chemical messages (hormones) that travel through the blood.
ANIMAL HORMONES
- Insulin: Produced by the pancreas.
- Regulates blood glucose levels.
- Facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells.
- Glucagon: Also produced by the pancreas
- Raises blood glucose levels.
- Stimulates the liver to release stored glucose.
- Adrenaline (Epinephrine): Produced by the adrenal glands.
- Prepares the body for “fight or flight” response.
- Increases heart rate, blood pressure, and energy availability.
- Thyroid Hormones: Produced by the thyroid gland.
- Regulates metabolism and energy levels.
- Influence growth and development.
- Oestrogen and Testosterone: Sex hormones that regulate reproductive functions and secondary sexual characteristics.
PLANT HORMONES
- Auxins: Promote cell elongation and growth. Involved in phototropism (growth towards light) and gravitropism (growth in response to gravity).
- Gibberellins: Stimulate stem elongation, seed germination, and flowering. Play a role in breaking dormancy in seeds.
- Cytokinins: Promote cell division and shoot development. Delay leaf senescence (ageing).
- Abscisic Acid (ABA): Inhibits growth and promotes seed dormancy. Helps plants respond to stress conditions (e.g., drought).
- Ethylene: Regulates fruit ripening and flower wilting. Involved in the response to mechanical stress.
8.7 THE SENSE ORGANS
Sense organs are specialized organs that detect and respond to specific types of stimuli, allowing organisms to interact with their environment.
TYPES OF SENSE ORGANS
- Eyes (Vision): Detect light and enable vision.
- Composed of structures such as the cornea, lens, retina, and optic nerve.
- Photoreceptors (rods and cones) in the retina convert light into electrical signals.
- Ears (Hearing and Balance): Detect sound waves and maintain balance.
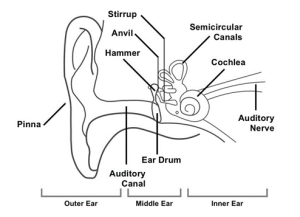
- Composed of the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear.
- Nose (Smell): Detects airborne chemicals and enables the sense of smell (olfaction).
- Olfactory receptors in the nasal cavity convert chemical signals into electrical impulses.
- Tongue (Taste): Detects dissolved substances and enables the sense of taste (gustation).
- Taste buds on the tongue contain receptors for sweet, sour, salty, bitter, flavours.
- Skin (Touch): Detects pressure, temperature, pain, and texture.
- Contains various receptors, including mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors, and nociceptors.
8.8 STRUCTURE OF THE EYE
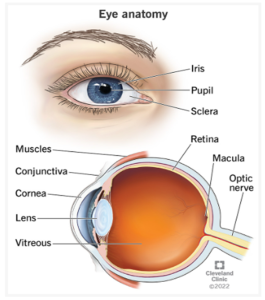
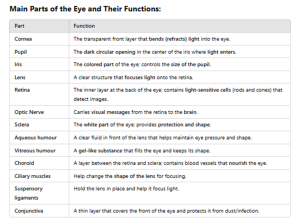
ADAPTATION OF THE EYE TO SHORT VISION (SHORT DISTANCE) – When focusing on nearby objects, the ciliary muscles contract, causing the lens to become thicker and more curved. This increased curvature allows for greater refraction of light, bringing the image into focus on the retina.
ADAPTATION OF THE EYES TO DISTANT VISION (LONG DISTANCE) – For distant objects, the ciliary muscles relax, allowing the lens to flatten, A flatter lens reduces the refraction of light, enabling the eye to focus on faraway objects clearly.
ROLE OF THE PUPIL – The pupil adjusts in size to control the amount of light entering the eye. In bright light, the pupil constricts to reduce light intake, while in dim light, it dilates to allow more light in, aiding in better vision at various distances.
PHOTORECEPTOR CELLS – The retina contains rods and cones that help in adapting to different light conditions and distances. Rods are more sensitive to light and help in low-light conditions, while cones are responsible for colour vision and function best in bright light.
8.9 EYE DEFECTS AND THEIR CORRECTIONS
- MYOPIA (Short-sightedness): Difficulty seeing distant objects clearly; nearby objects are seen clearly.
- Correction – Concave lenses (negative lenses) are used to diverge light rays, allowing them to focus correctly on the retina.
- HYPERMETROPIA (Farsightedness): Difficulty seeing close objects clearly; distant objects may be seen more clearly.
- Correction– Convex lenses (positive lenses) are used to converge light rays, helping them focus on the retina.
- ASTIGMATISM: Distorted or blurred vision due to an irregularly shaped cornea or lens.
- Correction – Cylindrical lenses are used to compensate for the uneven curvature of the cornea or lens, allowing for clearer vision.
- PRESBYOPIA: Age-related difficulty in focusing on close objects, often due to the loss of elasticity in the lens.
- Correction – Bifocal or multifocal lenses are used to provide different optical powers for distance and near vision.
- CATARACTS: Clouding of the lens, leading to decreased vision.
- Correction – Surgical removal of the cloudy lens and replacement with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL).
8.10 STRUCTURE OF THE EAR
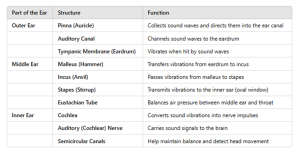
DIAGRAM OF THE EAR STRUCTURE
8.11 THE TONGUE
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth that plays a vital role in taste, chewing, swallowing, and speech. It is covered by a mucous membrane and contains specialized receptors for taste.
FUNCTIONS OF THE TONGUE
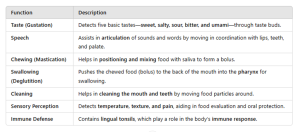
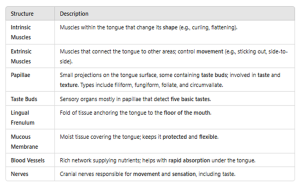
8.12 THE SKIN
The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It serves as a protective barrier between the internal organs and the external environment.
STRUCTURE OF THE SKIN
- Epidermis: The outermost layer of skin that provides a barrier and is responsible for skin tone. It contains keratinocytes, melanocytes, and Langerhans cells.
- Dermis: The middle layer that contains connective tissue, hair follicles, sweat glands, and blood vessels. It provides strength and elasticity to the skin.
- Hypodermis (Subcutaneous Layer): The deepest layer that consists of fat and connective tissue, providing insulation and cushioning for the body.
- Hair Follicles: Structures from which hair grows, playing a role in sensation and protection.
- Sebaceous Glands: Glands that secrete oil (sebum) to keep the skin moisturized.
ADAPTATION OF THE SKIN TO COLD WEATHER (Vasoconstriction) – Blood vessels in the skin narrow (constrict) to reduce blood flow, conserving body heat, resulting to shivering.
ADAPTATION OF THE SKIN TO HOT WEATHER (Vasodilation) – Blood vessels in the skin widen (dilate) to increase blood flow, allowing more heat to be released from the body, resulting to sweating.
POIKILOTHERMIC ORGANISMS – Poikilothermic organisms, also known as ectotherms, have body temperatures that vary with the temperature of their environment e.g, reptiles, amphibians, and most fish.
HOMEOTHERMIC ORGANISMS – Homeothermic organisms, also known as endotherms, maintain a relatively constant internal body temperature regardless of external environmental conditions e.g, mammals (like humans) and birds.
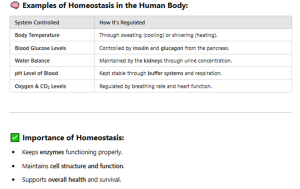
8.13 HOMEOSTASIS
Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of a stable internal environment of an organism despite external changes.
DTW Tutorials Study Resource Links;
First of All to obtain high JAMB &WAEC Scores, YOU HAVE TO Practice! Practice!! Practice!!
Use DTW JAMB & WAEC 2025 CBT Practice App!!!
– GET DTW TUTORIALS JAMB & WAEC 2025 CBT EXAM PRACTICE APP for all Subjects with over 31,000 Past Questions and Correct Solutions to Practice with offline! (Activation cost is N4000 for 1 year) Download Links Below for Mobile Phones & Laptop Computer;
DTW TUTORIALS JAMB 2025 APP For MOBILE Phone Direct Download link;
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.iafsawii.dtw.jamb
DTW TUTORIALS JAMB 2025 APP For DESKTOP Laptop Computer Direct Download link; https://drive.google.com/file/d/1iIHBoWjEeJeCFyTO9nt-9kAveH2FqjrT/view?usp=sharing
Download Links for WAEC 2025 App;
JAMB RESOURCE LINKS BELOW;
– JAMB Past Questions Solved Playlists on Math, Phy, Chem; https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLLgYU6fS5143-p4dfWIFL7keuB1SBgT2b
– THE LEKKI HEADMASTER – Summary, Questions And Answers (JAMB 2025 NOVEL); https://dtwtutorials.com/the-lekki-headmaster-jamb-2025-novel-summary-questions-and-answers-pdf-download/
– JAMB 2025 Recommended Text Books – https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-recommended-text-books-for-all-subjects/
– JAMB 2025 Syllabus all Subjects – https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-syllabus-free-download/
– JAMB 2025 Syllabus in 30 Days Timetable Challenge by DTW Tutorials for Science, Art & Commercial Subject Combinations – Cover Your JAMB Syllabus in 30 Days Challenge; https://dtwtutorials.com/jamb-2025-syllabus-in-30-days-timetable-challenge-by-dtw-tutorials-cover-your-jamb-syllabus-in-30-days-challenge/
– How to Manage Your Jamb Exam Time for High Scores; https://youtu.be/Tp4Va8haib8
– Physics Notes and Questions on All topics; https://dtwtutorials.com/category/tutorials/physics-tutorials/
– Chemistry Notes and Questions on All topics; https://dtwtutorials.com/category/tutorials/chemistry/
– How to Read, Understand and Remember Always- https://youtu.be/kL8BpRePudA
– How to Cover Your JAMB Syllabus Fast in 30 Days!!; https://youtu.be/RVgyn01Ptd0
– What to do a night before your Jamb Exam (+Exam Prayers); https://youtu.be/njbAx4Oz5Rw
– How to Manage Your Jamb Exam Time for High Scores; https://youtu.be/Tp4Va8haib8
– Overcoming Exam Fear/Anxiety– https://youtu.be/Uvf81rvd0ls
You can also join our online groups below for instant JAMB 2025 Updates;
Join DTW JAMB 2025 Intensive Tutorials Study Groups on Facebook, Telegram and WhatsApp Group;
Facebook Group – https://web.facebook.com/groups/dtwtutorialsgroup/
WhatsApp Group – https://chat.whatsapp.com/E8pprCQYtahKfpQN9UB0aU
Telegram Group – https://t.me/+AcXfhJPSIiI2ZTY0
WhatsApp Channel – https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029VaAWvTmDDmFT9o25dV3u
DTW JAMB 2025 Intensive Online Lessons/Tutorials
Online JAMB 2025 Tutorials – Your Path to Jamb Success!
Are you preparing for the JAMB 2025 Exam and aiming for excellence? Look no further than Online Jamb Tutorial by DTW Consult. We’re dedicated to helping you ace your Jamb with confidence.
- Why Choose DTW Online JAMB Intensive Tutorials?
• Engaging, Clear and Interactive Online Lectures
• Completion of JAMB Syllabus
• Weekly Quiz Assessments
• Continuous Brainstorming and Competitions
• Membership in an Active Learning Community
• Consistent Solving of JAMB Past Questions-
• Expert Jamb Instructors
• Comprehensive Study Materials - All Classes are Recorded!! In case you miss any class, and when you join us you will have access to all the previous class recorded videos!!!
• Subjects;
English
Physics
Chemistry
Biology
Math
Economics
Literature
Crs
Government
• Affordable Tuition – N7000 monthly (6pm – 10pm, Mon to Fri)
Lectures Ongoing! Register Now!!
Bank Details:
Account Name: DTW Consult
Account Number: 6414330770
Bank: Moniepoint
Amount – N7000
For easy payment and enrollment.
Proof of payment should be sent by WhatsApp.
Contact Us:
WhatsApp: 09085099582, 08038732879
Email: dtwconsultng@gmail.com
Take a step closer to your Jamb success with DTW Online Jamb 2025 Intensive Tutorials.
Let’s work together to unlock your full potential!

https://youtu.be/P7wtBH46ZMMnsive Tutorials. Let’s work together to unlock your full potential! #JambPrep #OnlineTutorial #DTWConsult #JambSuccess #jamb2025 #utme2025

No Comments